EDB Postgres AI AI/ML - Overview
At the heart of EDB Postgres® AI is the EDB Postgres AI database (aidb). This builds on Postgres's flexibility and extends its capability to include storing the vector data of embeddings.
The aidb extension is currently available as a tech preview. It will be continuously extended with new functions. This overview presents the functionality available to date.
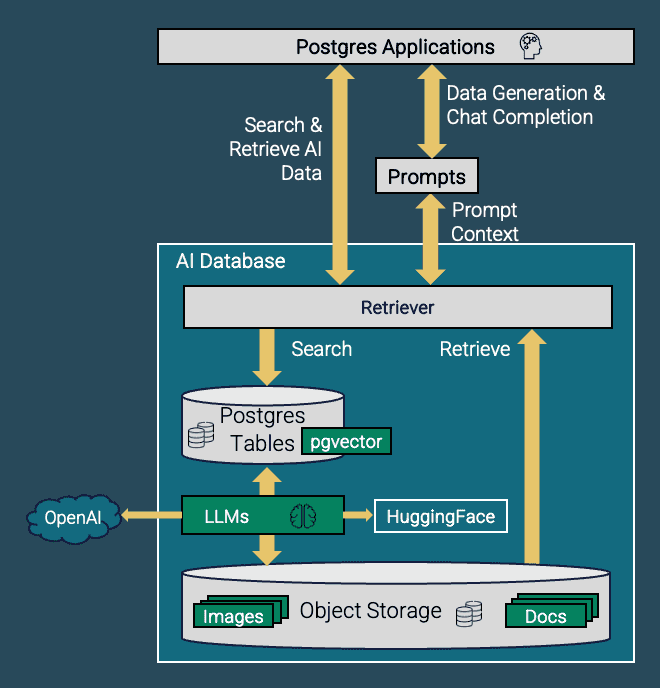
aidb introduces the concept of a “retriever” that you can create for a given type and location of AI data. Currently aidb supports unstructured plain text documents as well as a set of image formats. This data can either reside in regular columns of a Postgres table or it can reside in an S3 compatible object storage bucket.
A retriever encapsulates all processing that is needed to make the AI data in the provided source location searchable and retrievable through similarity. The application just needs to create a retriever via the aidb.create_retriever() function. When auto_embedding=TRUE is specified the aidb extension will automatically generate embeddings for all the data in the source location.
Otherwise it will be up to the application to request a bulk generation of embeddings using aidb.refresh_retriever().
Auto embedding is currently supported for AI data stored in Postgres tables and it automates the embedding updates using Postgres triggers. You can also combine the two options by using aidb.refresh_retriever() to embed all previously existing data and also setting auto_embedding=TRUE to generate embeddings for all new and changed data from now on.
All embedding generation, storage, indexing, and management is handled by the aidb extension internally. The application just has to specify the encoder LLM that the retriever should be using for this specific data and use case.
Once a retriever is created and all embeddings are up to date, the application can just use aidb.retrieve() to run a similarity search and retrieval by providing a query input. When the retriever is created for text data, the query input is also a text term. For image retrievers the query input is an image. The aidb retriever makes sure to use the same encoder LLM for the query input, conducts a similarity search and finally returns the ranked list of similar data from the source location.
aidb currently supports a broad list of open encoder LLMs from HuggingFace as well as a set of OpenAI encoders. Consult the list of supported encoder LLMs in the aidb.encoders meta table. HuggingFace LLMs are running locally on the Postgres node, while OpenAI encoders involve a call out to the OpenAI cloud service.
Could this page be better? Report a problem or suggest an addition!