Fault injection testing
You can test the fault tolerance of your cluster by deleting a VM to inject a fault. Once a VM is deleted, you can monitor the availability and recovery of the cluster.
Requirements
Before using fault injection testing, ensure you meet the following requirements:
- You've connected your Cloud Service account with your Azure subscription. See Connecting to your Azure cloud for more information.
- You have permissions in your Azure subscription to view and delete VMs and also the ability to view Kubernetes pods via Azure Kubernetes Service RBAC Reader.
- You have PGD CLI installed. See Installing PGD CLI for more information.
- You've created a
pgd-cli-config.ymlfile in your home directory. See Configuring PGD CLI for more information.
Fault injection testing steps
Fault injection testing consists of the following steps:
- Verifying cluster health
- Determining the write leader node for your cluster
- Deleting a write leader node from your cluster
- Monitoring cluster health
Verifying cluster health
Use the following commands to monitor your cluster health, node info, raft, replication lag, and write leads:
pgd check-health -f pgd-cli-config.yml pgd verify-cluster -f pgd-cli-config.yml pgd show-nodes -f pgd-cli-config.yml pgd show-raft -f pgd-cli-config.yml pgd show-replslots –verbose -f pgd-cli-config.yml pgd show-subscriptions -f pgd-cli-config.yml pgd show-groups -f pgd-cli-config.yml
You can use pgd help for more information on these commands.
To list the supported commands, enter:
pgd helpFor help with a specific command and its parameters, enter pgd help <command_name>. For example:
pgd help show-nodesDetermining the write leader node for your cluster
This example shows the command for determining the write leader node for a cluster:
pgd show-groups -f pgd-cli-config.ymlGroup Group ID Type Write Leader -------- ------------------ —--- ------------ world 3239291720 global p-x67kjp3fsq-d-1 p-x67kjp3fsq-a 2456382099 data world p-x67kjp3fsq-a-1 p-x67kjp3fsq-c 4147262499 data world p-x67kjp3fsq-d 3176957154 data world p-x67kjp3fsq-d-1
In this example, the write leader node is p-x67kjp3fsq-a-1.
Deleting a write leader node from your cluster
To delete a write lead node from the cluster:
Log into Console.
In a separate browser window, log into your Microsoft Azure subscription.
In the left navigation of Console, select Clusters.
Select the cluster to test fault injection with and copy the string value from the URL. The string value is located after the underscore.
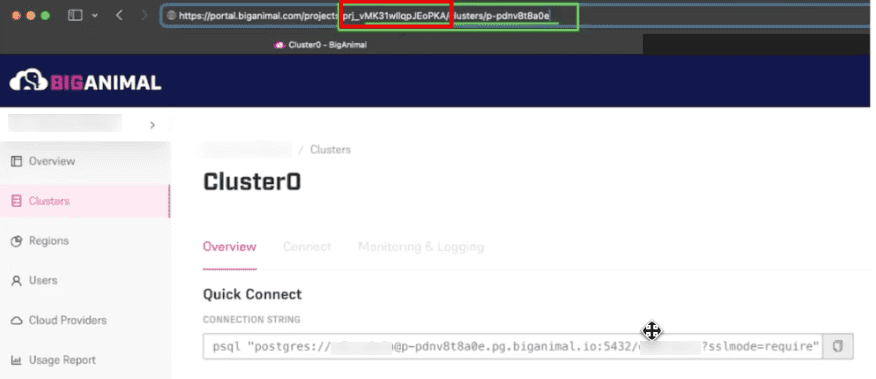
To search for the data plane, in your Azure subscription, paste the string into the search and prefix it with
dp-.From the results, select the Kubernetes service from the Azure region that your cluster is deployed in.
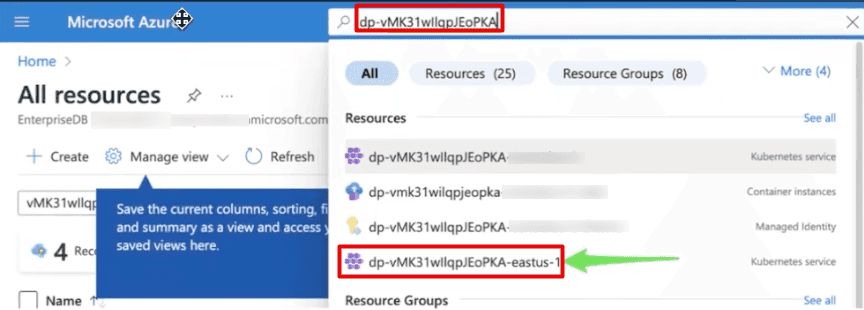
Identify the Kubernetes service for your cluster.
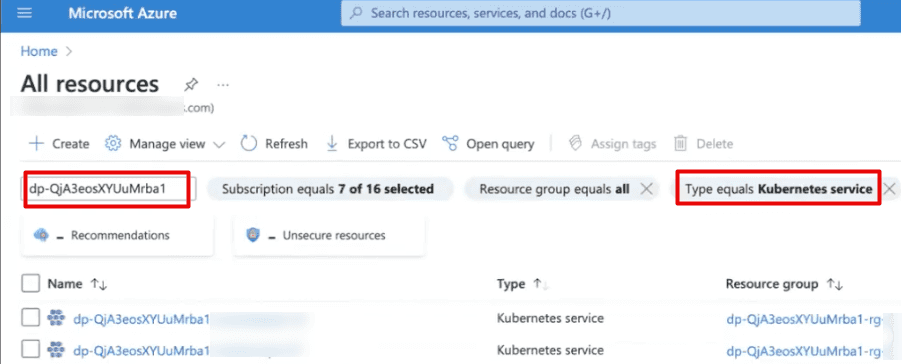
Note
Don't delete the Azure Kubernetes VMSS here or sub resources directly.
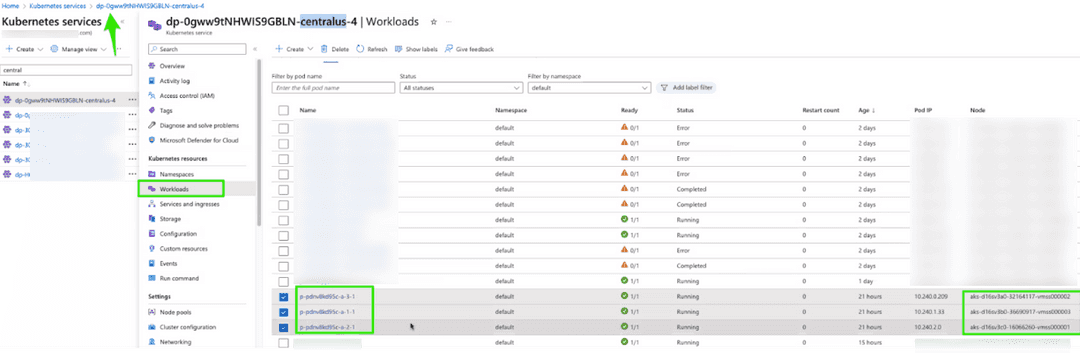
- To delete a chosen node, browse to the data plane, select Workloads, and locate the Kubernetes resources for your cluster.
Monitoring cluster health
After deleting a cluster node, you can monitor the health of the cluster using the same PGD CLI commands that you used to verify cluster health.
Could this page be better? Report a problem or suggest an addition!