Failover Manager with EDB PgBouncer v4
You can use Failover Manager and EDB PgBouncer to provide high availability in an on-premises setup as well as in a cloud setup. EDB PgBouncer is a popular connection pooler, but it is not enough to achieve PostgreSQL high availability by itself as it doesn't have multi-host configuration, failover, or detection.
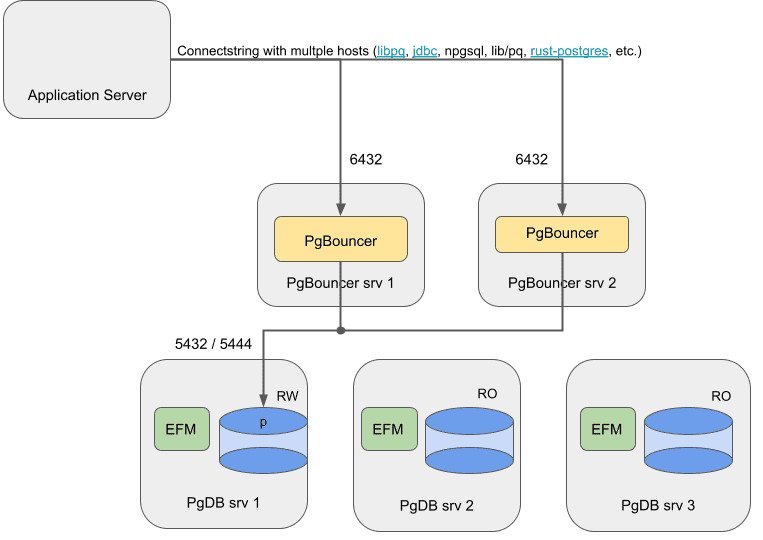
Failover Manager with EDB PgBouncer on premises
For an on-premises setup, use the connection libraries to provide high availability by using a connection string with multiple hosts.
Failover Manager with EDB PgBouncer in the cloud
For a cloud setup, use a network load balancer (NLB) to balance the traffic on both instances of EDB PgBouncer.
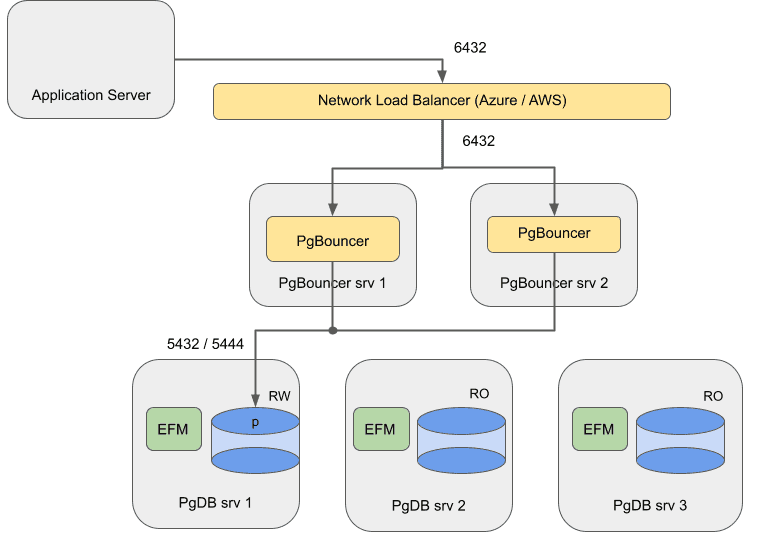
EDB does not support this architecture with EDB PgBouncer and Failover Manager/PostgreSQL running on the same machines:
A restriction with cloud network load balancers Azure doesn't route traffic properly when source and destination reside on the same machines.
In a mixed architecture, traffic between EDB PgBouncer and Postgres can become unbalanced (sometimes local, sometimes networked).
EDB PgBouncer and PostgreSQL compete for resources.
A master failure impacts both routing (EDB PgBouncer) and database when these two components are combined on the same machines.
Using Failover Manager with PgBouncer
Installing
Install and configure Advanced Server database, Failover Manager, and EDB PgBouncer on AWS virtual machines as follows:
| Systems | Components |
|---|---|
| PgDB srv 1, 2, 3 | Primary / standby node running Advanced Server and Failover Manager |
| PgBouncer srv 1, 2 | PgBouncer node running EDB PgBouncer 1.15. Register these two nodes as targets in the target group. Two is the minimum and is sufficient for most cases. |
Configuring Failover Manager
Use the instructions provided in the Failover Manager documentation to configure Failover Manager. Perform the following steps in addition to those instructions:
- Create an integration script that connects to every (remote)
EDB PgBouncer host and runs the redirect script. Locate the script at
/usr/edb/efm-4.2/bin/efm_pgbouncer_functions. Make sure the user efm can execute the script, which has the following contents:
#!/bin/bash -x
set -e
IFS=', ' read -r -a PGB_HOSTS <<< "$4"
FAILED_PGB_HOST=''
for PGB_HOST in "${PGB_HOSTS[@]}"; do
echo "redirecting to '$2' on enterprisedb@${PGB_HOST}"
if [ "$3" == "p" ]; then
ssh "enterprisedb@${PGB_HOST}" /usr/edb/pgbouncer1.15/bin/redirect.sh "$2" || FAILED_PGB_HOST="$FAILED_PGB_HOST $PGB_HOST" < /dev/null
fi
done
# return exit code to inform EFM agent about failure. The agent would send a failure
# notification accordingly for manual intervention
if [ ! -z "$FAILED_PGB_HOST" ]; then
echo "Failed to redirect to '$2' on '$FAILED_PGB_HOST'"
exit 1
fi
- On each database node, set
script.load.balancer.attachto the custom script in theefmproperties file:
script.load.balancer.attach=/usr/edb/efm-4.2/bin/efm_pgbouncer_functions attach %h %t <pgbs1>,<pgbs2>
<pgbs1> is the hostname or IP address for PgBouncer server 1 and <pgbs2> is the hostname or IP address for PgBouncer server 2.
Configuring PostgreSQL
During normal operation, traffic is balanced across both PgBouncer instances, and both open connections to PostgreSQL.
Therefore, make sure that in PostgreSQL the max_connections parameter is compensated to accept enough connections from both instances.
Configuring EDB PgBouncer
You can use the instructions provided in the EDB PgBouncer documentation to configure EDB PgBouncer. Perform the following steps in addition to those instructions:
- Append the following line to the
edb-pgbouncer-1.15.inifile:
%include /etc/edb/pgbouncer1.15/edb-pgbouncer-databases.ini- In the
edb-pgbouncer-1.15.inifile, set the value oflisten_addrto *:
listen_addr = *Leave the [databases] section empty in the
edb-pgbouncer-1.15.inifile, and configure this section in a separate file/etc/edb/pgbouncer1.15/edb-pgbouncer-databases.ini. Ensure that this extra config file is readable and writable by enterprisedb.The following is an example of the bash commands to create the file:
echo "[databases]" > /etc/edb/pgbouncer1.15/edb-pgbouncer-databases.ini
echo "edb= host=srv1" >> /etc/edb/pgbouncer1.15/edb-pgbouncer-databases.ini
chown enterprisedb: /etc/edb/pgbouncer1.15/edb-pgbouncer-databases.ini- Create a script
/usr/edb/pgbouncer1.15/bin/redirect.shto use to reconfigure the databases chapter and reload pgbouncer. Make sure the script is owned by root and that user/group/other (0755) has read and execute access. The script has the following content:
#!/bin/bash
set -e
#Some defaults
PGBOUNCER_DATABASE_INI=/etc/edb/pgbouncer1.15/edb-pgbouncer-databases.ini
PGMSTR=${1:-localhost}
# enterprisedb user does not have permissions to write in folder directly, so `sed -i` will not work
TMPFILE=$(mktemp)
sed "s/host=[A-Za-z0-9.]*/host=${PGMSTR}/" "${PGBOUNCER_DATABASE_INI}" > "${TMPFILE}"
if ! diff -q "${PGBOUNCER_DATABASE_INI}" "${TMPFILE}" >/dev/null; then
cat "${TMPFILE}" > "${PGBOUNCER_DATABASE_INI}"
pkill -SIGHUP pgbouncer
fiConfiguring passwordless ssh
For the EDB PgBouncer integration, passwordless ssh access is required. There are multiple ways
to configure ssh. Follow your organization's recommended process to
configure the passwordless ssh. For a quick start, you can also follow this example for configuring passwordless ssh.
The user efm user must be able to ssh as the user running PgBouncer; for example, enterprisedb.
Configure on EDB PgBouncer hosts
On every EDB PgBouncer host, temporarily set a password for the enterprisedb user. As root, run
passwd enterprisedband enter the temporary password twice.Make sure that passwordless
sshis enabled. You can check with the following command:grep ^PasswordAuthentication /etc/ssh/sshd_configMake sure it is set to
yes. If needed, change it and restartssh.
Configure on Failover Manager/PostgreSQL hosts
On every Failover Manager/postgres host, as the efm user:
- Run the following command:
ssh-keygen -P "" -f ~/.ssh/id_rsa
- For every EDB PgBouncer host, copy the
sshkey with the following command:The default home directory for thessh-copy-id enterprisedb@<pgbouncerhost>
enterprisedbuser is/var/lib/edb. If this directory is not already present, create it manually. As a sudo user, run the following commands on each EDB PgBouncer host:mkdir -p /var/lib/edb chown -R enterprisedb:enterprisedb /var/lib/edb
Resetting temporary passwords on EDB PgBouncer hosts
You can reset the temporary password for the enterprisedb user on every EDB PgBouncer host by running the following command as root:
passwd -d enterprisedb
Configuring the network load balancer
For the Failover Manager \ EDB PgBouncer integration using a network load balancer in AWS or Azure, you need to perform additional steps.
Add the following rules to the security groups to be used by the EDB PgBouncer and database instances.
Rules for the security group to be used by the EDB PgBouncer instances (SG PgBouncer).
Type Protocol Port range Source Description Custom TCP TCP 6432 Entire Subnet PgBouncer Custom TCP TCP 22 Entire Subnet ssh
In addition to these rules, add the rules for SSH and Ping as per your requirement.
Rules for the security group used by the database instances (SG DB):
Type Protocol Port range Source Description Custom TCP TCP 7800 Entire Subnet Failover Manager Custom TCP TCP 5444 Entire Subnet Postgres Custom TCP TCP 22 Entire Subnet ssh
These rules ensure that the ports required to run the database, Failover Manager, and EDB PgBouncer are open for communication between the nodes and the load balancer for traffic routing and health monitoring.
In addition to these rules, add the rules for SSH and Ping as per your requirement.
Configuring NLB in Azure
If you are using AWS, see Configuring NLB in AWS.
After configuring the rules described in Creating rules for security groups, follow the Azure documentation to:
Create a backend pool consisting of the two virtual machines running the EDB PgBouncer instances. Use the private IPs of the virtual machines to create the backend pool.
Add a health probe to check if the EDB PgBouncer instance is available on the virtual machines. Select
TCPas the protocol and6432as the port.Add a load balancing rule for port
6432. This rule ensures that the network traffic coming toward that port is distributed evenly among all the virtual machines present in the backend pool. SelectPublicload balancer orInternalload balancer as the type.
After completing these configurations, you can connect to the database
on the IP address of the network load balancer using port 6432. If a
failure occurs on the primary database server, Failover Manager
promotes a new primary and then reconfigures EDB PgBouncer to redistribute
traffic. If any of the EDB PgBouncer processes is not available to
accept traffic, the network load balancer redistributes all
the traffic to the remaining EDB PgBouncer processes. Make sure that the
max_client_conn parameter is tuned to compensate for the higher number
of connections in case of failover.
Configuring NLB in AWS
The following sample configuration assumes:
All the EC2 instances and the load balancer are deployed in the same subnet. If required, you can add the database nodes to another subnet, but that requires a more complex configuration and might have a performance impact.
There's a security group for PgBouncer and a security group for the database instances.
After configuring the rules described in Creating rules for security groups, follow the AWS documentation to
Create a target group with the following details:
Name Type Protocol Port VPC pgbouncer Instances TCP 6432 Select the VPC to which the instances are connected. Leave the rest of the settings (Health check TCP and Advanced health check settings) as default.
Register the created target groups with the instances that are running EDB PgBouncer.
Create a load balancer with the following details:
Type VPC Listener PublicorInternal. EDB recommends using an internal load balancer.Choose a VPC and map it to the desired zones. Create a listener with TCPas6432, and forward it to the target group pgbouncer.
After completing the configurations, you can connect to the database on
the IP address of the network load balancer on port 6432. If a failure
occurs on the primary database server, Failover Manager promotes a new
primary and then reconfigures EDB PgBouncer to redistribute traffic. If any
of the EDB PgBouncer processes is not available to accept traffic, the network
load balancer redistributes all the traffic to
the remaining EDB PgBouncer processes. Make sure that the max_client_conn
parameter is tuned to compensate for the higher number of connections in
case of failover.